Active Metadata – What It Is and Why It Matters
For the past several years we have been subjected to various analogies invoked to convey the growth in data we are experiencing – from avalanche to tsunami, oddly all related to natural disasters. While we are getting jaded by these tropes, the underlying problem, however, is real. The data we have access to as part of our organizations is growing exponentially in volume and complexity, and the effort to harness it to propel digital transformation initiatives is increasing rapidly. But even at the granular level, understanding data can be difficult. Consider a single attribute like Gender, which can have multiple values across data sets. Some data sets containing Gender may have 3 values, some 5, and others 10. Metadata helps explain these variations across data sets and brings awareness to the data as a whole. Digital transformation requires us to understand data and use it innovatively and efficiently; the key component that can help in improving the efficiency of such data-driven initiatives is active metadata.
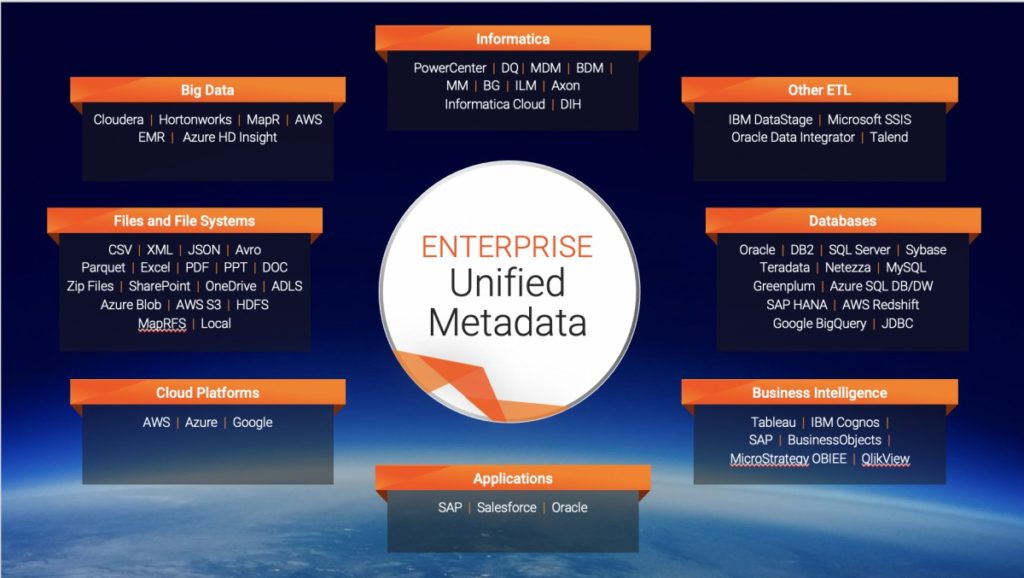
These days, while we are seeing an increased interest in metadata it is still mostly an afterthought or worse, the untapped effluent of a data management implementation. However, active metadata is a vital foundation and semantic layer of a well-architected data management system, which yields surprising benefits across the lifecycle of data projects. Metadata provides a means to understand all the information available in an enterprise, its quality, and relevance. Metadata’s value grows even more if it is active - overlaid with machine learning , augmented with human knowledge, and integrated. It makes the wider data management processes intelligent and dynamic. As an example, metadata can highlight missing, incorrect, or anomalous data. It can then help improve the quality of analytics where the data behind a report is automatically corrected and enriched to improve decision making and avoid costly mistakes. (Metadata management is an essential part of a System Thinking approach to data. To learn more, read this blog post about System Thinking for data and why it’s so important for data leaders.)
How to maximize the benefits of your metadata
To maximize the benefits of a metadata foundation we need to tap into four major categories of metadata:
- Technical: Database schemas, mappings and code, transformations, quality checks
- Business: Glossary terms, governance processes, application and business context
- Operational & infrastructure: Run-time stats, time stamps, volume metrics, log information, system and location information
- Usage: User ratings, comments, access patterns
The process to bring metadata across these four categories together into a common and shared metadata layer should include these 3 steps:
- Collect: Scan the metadata from all your enterprise’s data systems including databases and filesystems, integration processes, analytics and data science tools with as much fidelity as possible.
- Curate: Document a business view of data with glossary terms, concepts, relationships and processes. Augment the collected metadata with this business context. Gather additional input from users in terms of rating and comments to help assess the usefulness of data assets to the end users.
- Infer: Apply intelligence to derive relationships not obvious in the collected metadata like data lineage and similarity, determine and ranking the most useful data sets for different users.
By gathering technical, business, operational and usage metadata we create a knowledge graph of an enterprise’s data assets with their relationships. This metadata graph is made active when you apply AI and machine learning and integrate it with data management solutions. Active metadata makes it easier, efficient, and automated for users to build, deploy, and operate data management applications for analytics, data science, governance, or almost any other purpose.
A great way to achieve active metadata is by implementing an enterprise data catalog and ensuring it is integrated into your data processes. In fact, analyst firm Gartner advises its clients to “Favor providers of data integration tools that exhibit a clear roadmap showing how active metadata-driven ML enables better business outcomes or service levels.”[1]
Consider the benefits active metadata provides:
- Identifies the appropriate data suitable for a specific business purpose
- Automatically integrates systems based on learned patterns and adjusts for external changes
- Provides the business context to the data required to increase confidence in analytics
- Locates and enriches the attributes of Master Data Models like Customer, Product, Vendor
- Documents and identifies data for driving collaborative data governance and compliance processes
- Highlights data quality and data privacy issues and the adherence of data to governance rules
- Cuts down development and maintenance effort for data integration pipelines
- Uses data relationships to identify new features for enriching data science models
- Enables self-service by provided the right data context for users
Data is considered the currency of business driving all digital transformation. An intelligent metadata layer, constructed, inferred, enriched, provides both deep insight into your rapidly growing data as well as maximizes the use and value of this data. Active metadata is indispensable for developing secure, efficient, and elegant data applications taking full advantage of the vast amount of data that is now available to business.
Read more about System Thinking in our blog series:
- What Is System Thinking for Data (And Why Is It So Important)?
- Top 10 Principles of an Intelligent Data Platform
- The 3 Principles of DataOps to Operationalize Your Data Platform
- 4 Ways AI Puts Rocket Fuel in Your Data Management
[1] Gartner, “Predicts 2019: Data Management Solutions,” Ted Friedman, Donald Feinberg, Mark Beyer, et al. 6 December 2018







