Big Data Management and Ranger Integration

Informatica Big Data Management (BDM) product is GUI based integrated development environment that organizations use to build their Data Integration, Data Quality and Data Governance processes for their big data platforms. Informatica BDM has built-in Smart Executor that supports various processing engines such as Blaze, Apache Spark, Apache Hive on MapReduce and Apache Hive on Tez. Informatica BDM can be used to perform data ingestion into a Hadoop cluster, data processing on the cluster and extraction of data from the Hadoop cluster. In Blaze mode, the Informatica mapping is processed by BlazeTM – Informatica’s native engine that runs as a YARN based application. In Spark mode, the Informatica mappings are translated into Scala code and in Hive on MapReduce mode, Informatica’s mappings are translated into MapReduce code and are executed natively to the Hadoop cluster. Informatica BDM integrates seamlessly with Hortonworks Data Platform (HDP) Hadoop cluster in all related aspects including its default authorization system: Ranger. Ranger can be used to enforce a fine-grained role based authorization to data as well as metadata stored inside the HDP cluster. This document explains in detail how Informatica BDM’s various processing engines integrate with Ranger.
Authentication
Authentication is the process of reliably ensuring the user is who he/she claims to be. Kerberos is the widely accepted authentication mechanism on Hadoop including Hortonworks Data Platform. Kerberos protocol relies on a Key Distribution Center (KDC), a network service which issues tickets permitting access. Informatica BDM supports Kerberos authentication on both Active directory and MIT-based key distribution centers. Kerberos authentication is supported by all modes of execution in Informatica BDM.
Authorization
Authorization is the process of determining whether or not a user has access to perform certain operations on a given system. In HDP Hadoop clusters, authorization plays a vital role in ensuring the users access only the data that they are allowed to by the Hadoop administrator.
Blaze - A YARN Application
When executing mappings on Informatica Blaze, optimizer first makes an invocation to Hadoop Service to fetch metadata information such as hive table’s partitioning details. Then the job is submitted to Blaze Runtime. The illustration below represents how Blaze interacts with the Hadoop Service, such as Hive Server 2. When an Informatica mapping gets executed in Blaze mode, call is made to the Hive Metastore (if Hive sources/targets are involved) to understand the structure of the tables. The Blaze runtime then loads the optimized mapping into memory. This mapping then interacts with the corresponding Hadoop service to read the data or write the data. The Hadoop service itself is integrated with Ranger and ensures the authorization is taken place before the request is served. Blaze mode of execution is available starting with Version 10.0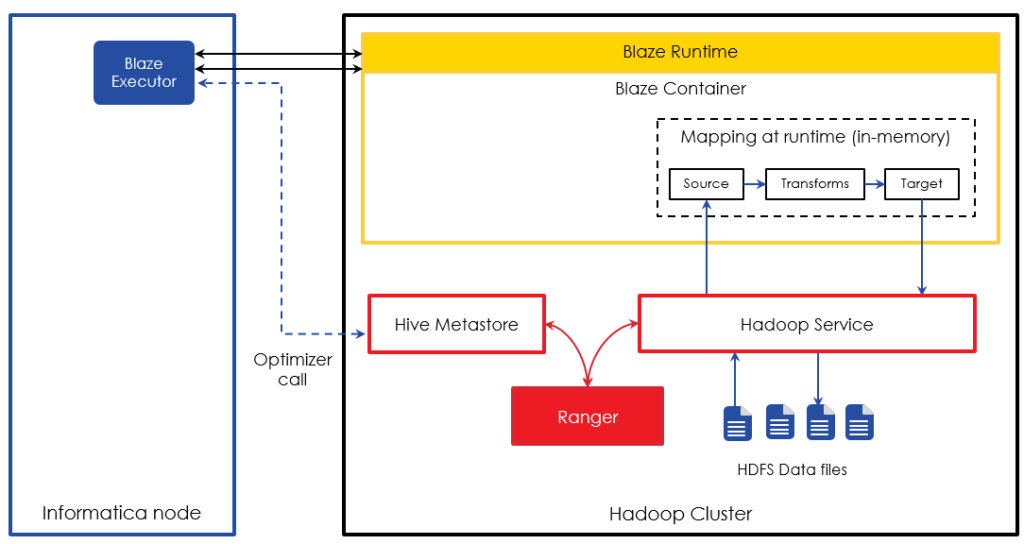
Spark
Informatica BDM can execute mappings as Spark’s Scala code on the HDP Hadoop cluster. The illustration below details different steps involved when using Spark execution mode. In this mode, the Spark executor translates Informatica’s mappings into Spark Scala code. As part of this translation, if Hive sources/targets are involved, Spark executor makes call to Hive metastore to understand the structure of the Hive tables and optimize the Scala code. This Scala code is then submitted to YARN for execution. When the Spark code accesses the data, corresponding Hadoop service relies on Ranger for authorization.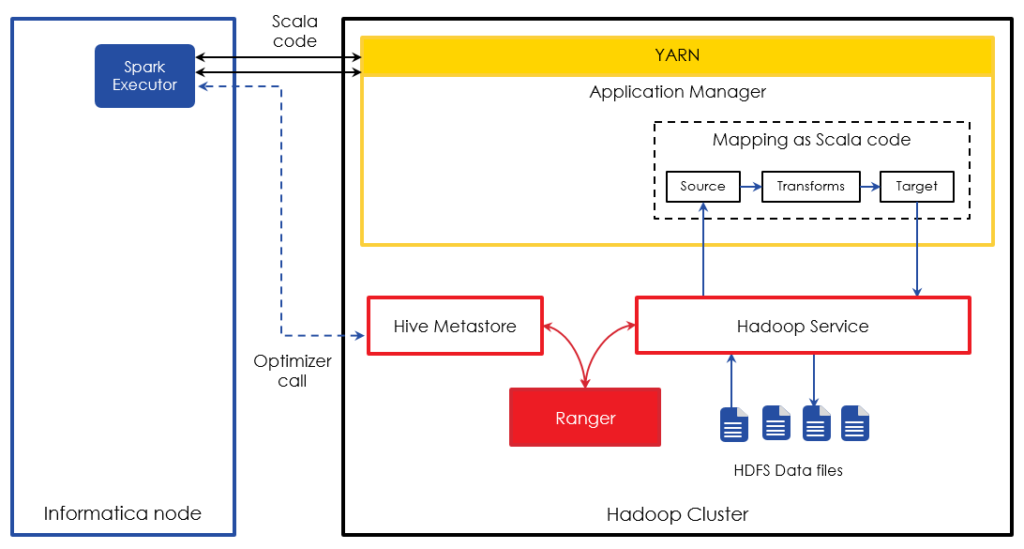
Hive on MapReduce
Informatica BDM can execute mappings as MapReduce code on the Hadoop cluster. Below illustration details different steps involved when using Hive on MapReduce mode. 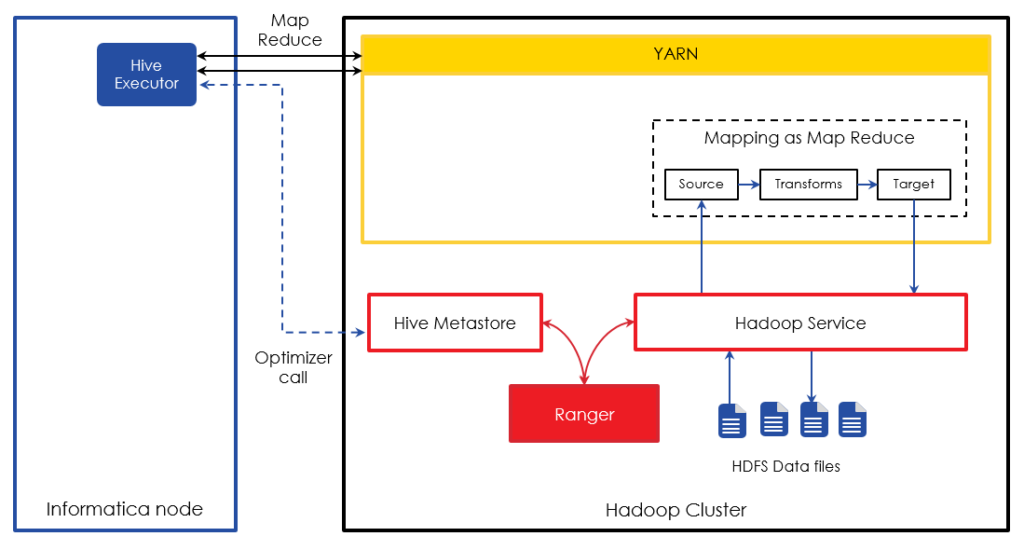 When a mapping is executed in Hive on MapReduce mode, the Hive executor on the Informatica node translates the Informatica mapping into MapReduce and submits the job to the Hadoop cluster. If Hive sources/targets are involved, the Hive executor makes a call to the Hive metastore to understand the table structure and optimize the mapping accordingly. As the MapReduce interacts with Hadoop services such as HDFS and Hive, the Hadoop service authorizes the requests with Ranger
When a mapping is executed in Hive on MapReduce mode, the Hive executor on the Informatica node translates the Informatica mapping into MapReduce and submits the job to the Hadoop cluster. If Hive sources/targets are involved, the Hive executor makes a call to the Hive metastore to understand the table structure and optimize the mapping accordingly. As the MapReduce interacts with Hadoop services such as HDFS and Hive, the Hadoop service authorizes the requests with Ranger
Hive on Tez
Tez can be enabled in Informatica BDM by a configuration change and is transparent to the mapping developed. Hence mappings running on Hive on Tez follow a similar pattern as Hive on MapReduce. When a mapping is executed in the Hive on Tez mode, the Hive executor on the Informatica node translates the Informatica mapping into Tez job and submits it to the Hadoop cluster. If Hive sources/targets are involved, the Hive executor makes a call to the Hive metastore to understand the table structure and optimize the mapping accordingly. As the Tez job interacts with Hadoop services such as HDFS and Hive, the Hadoop service authorizes the requests with Ranger.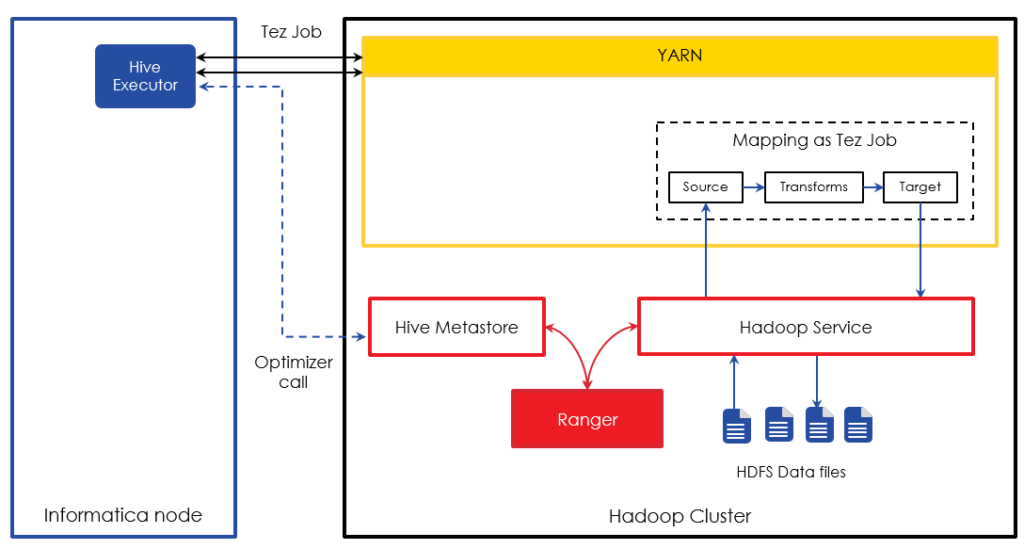
Summary
Informatica’s BDM integrates with Ranger in all modes of execution. Informatica’s BDM has Smart Executor that enables organizations to run their Informatica mappings seamlessly on one or more modes of execution under the purview of their existing security setup.







