What Does a Next-gen MDM Solution Look Like? End-to-End Capabilities (Part 1)

Master data management (MDM) technology is entering a new stage of maturity. Driven by the rising demands of Cloud and big data, today’s MDM is drastically different, offering greater capabilities, Hybrid deployment options, and more user flexibility than ever before.
The market forces that have shaped the MDM evolution are complex and include:
- The need for companies to differentiate on customer experience
- Increased regulations
- Growth strategies driven by mergers and acquisitions, and more.
But the result is a new generation of MDM solutions that must help organizations create new and improved business outcomes. To help navigate the evolution of MDM, I’ll be publishing a four-part blog series: “Understanding Next-Gen MDM.” This first installment of the series focuses on how modern MDM is developing end-to-end capabilities to address the needs influenced by big data, mobile, social media, and hybrid deployment options.
The First Generation of MDM (Late 1990s – 2008)
Before, when big data and cloud were in their infancy, data management had relatively simple requirements. We used MDM technology to “match and merge” data records, performing routine tasks such as:
- Identifying missing or erroneous entries
- Validating addresses or phone numbers
- Eliminating duplicate records
- Cleansing names and addresses
The automation of these tasks was a huge time-saver for organizations. This dramatically increased the overall quality of their customer data, but its impact on business processes was less apparent. That’s because MDM users were limited to a few scattered data stewards. Their job was to make sure match-and-merge batch jobs ran smoothly. And if any records failed the automation rules, they manually resolved the data conflicts on a case-by-case basis.
As data management experts, these data stewards didn’t require an intuitive user experience. The tools were built for them. And as the only users, some even learned how to write scripts to increase the functionality of the tool, with less need for graphical user interfaces.
The Second Generation of MDM (2008-2015/16)
Around 2010, we saw a shift in MDM. Many early adopters who built MDM for feeding data to Enterprise Data Warehouses and other reporting needs felt MDM needed to be operationalized across organizations. Companies wanted to unlock the full potential of MDM by delivering trusted data to every business process.
The consolidation also happened in the form of integrating multiple point MDM solutions used for customer data, product data etc. into a single solution. The multi-domain use cases emerged, helping companies better manage relationships that mattered the most. Questions that were hard to answer before — like, which customer bought which products? —could be answered easily now.
The user interface evolved as well. But for the most part remained focused on data stewards, not business users.
Entering the Next Generation of MDM (The new age, starting…NOW)
As we enter this new era of MDM, where all your data is big data, three big problems emerge:
- First, traditional match-and-merge alone no longer cuts it in this new world. Everything from web page clickstreams to social media activities to transactions and customer service interactions become fodder for customer intelligence—creating new requirements for data management capabilities.
- Second, data insights must be served directly to business users across organizations. Data stewards can no longer be the gatekeepers of MDM tools. Therefore, MDM tools must expand back-end capabilities to scale and undergo a massive front-end makeover to become faster, easier, and more intuitive to use.
- Third, MDM must support a hybrid world, providing the flexibility for customers to deploy on premise, in the cloud (including Hadoop), or in a hybrid deployment environment.
In other words, MDM must be more user-friendly, adaptable, and scalable across organization.
MDM: All grown up
Reflecting a successful (if not occasionally bumpy) adaptation to complex market pressures, today’s MDM is both highly capable and much easier to use. Supporting our new data era, it provides a rich, comprehensive view of the customer, supplier, patient, citizen, product, asset, and dozens of other master data entities by combining traditional transactional data with a wide variety of other data. Thanks to master data-fueled applications, today’s MDM delivers data intelligence that can be consumed—with minimal training—by a broad range of business professionals, from sales reps to marketers to customer service reps.
325 million business people are users of managed data.
The key to MDM’s generational shift, though, lies in fostering data from inception to consumption—and improving that data along the way. These end-to-end data management capabilities make modern MDM invaluable. Some of the most important end-to-end capabilities include:
- Discover and Model—With so much data available from so many sources, MDM must discover untapped sources of relevant data, even when they are not obvious or easy to find. Similarly, it must infer and suggest the best format for managed attributes (e.g., recommend the optimal model for a customer record).
- Cleanse and Enrich—Modern MDM comes with embedded data quality and data enrichment capabilities to improve the overall quality of data. It provides a seamless experience across the solution, checks for incomplete or invalid entries, and attempts to resolve conflicts. Having cleansed the data, it can now make the data more useful by adding missing information to the records, enriching them with information from other sources.
- Match and Merge—While MDM has expanded beyond its humble beginnings, validating (match) and deduplicating (merge) data is still needed as much as ever before. Once the duplicated profiles are identified, companies also need a robust, flexible, reliable framework to adapt to new types and sources of data attributes when determining survivorship to build the gold (master) record.
- Relate—Data is not an island. Its value is amplified exponentially when you capture its relationships to other data. For example, when a customer purchases a product, it’s useful to have a single view of that customer and that product. But the value to the business is huge when you define a relationship between those records (customer and product). MDM delivers these relationship insights to the business. This is especially critical when managing customer data. Information such as whom the customer lives with or works for can be vital to understanding that customer and providing better recommendations and service.
- Secure—MDM ensures that data conforms to business rules, which helps enforce regulatory compliance, as well as security and privacy
- Deliver—The value of any master data is realized when that data is delivered to the right people, supporting the right processes, at the right time, and in the right context. MDM ensures that data gets delivered as needed to customers, employees, applications, and analytics systems throughout the organization.
- Governance and Stewardship—MDM helps master data, turning it into an effective strategic asset. It allows companies to access the risk associated with that data, helps define policies, and helps monitor data quality. It supports effective stewardship of data by providing intuitive ways to evaluate, prioritize, and fix data issues.
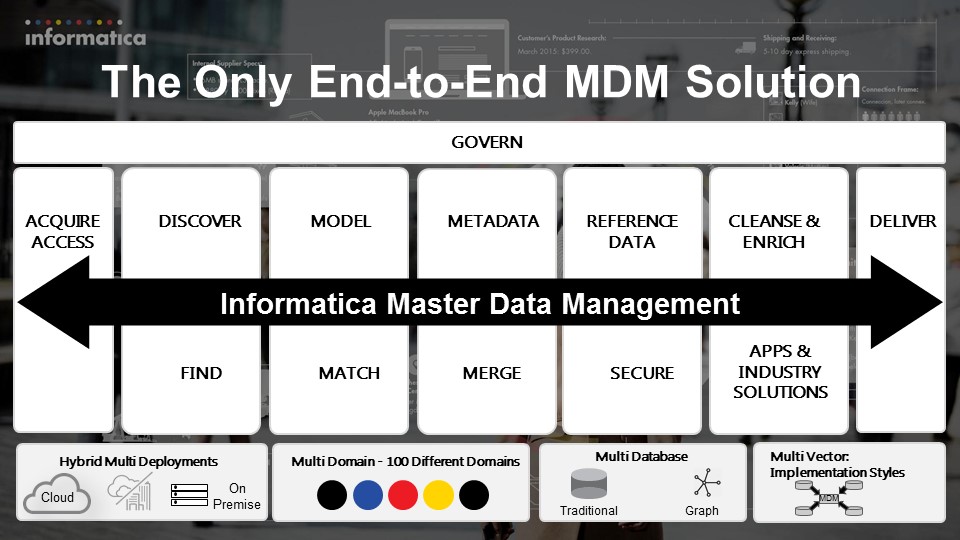
End-to-end MDM is the new standard for performance in data management and includes many important capabilities that go way beyond ‘match and merge.’
End-to-end capabilities fuel “new world” data management
As organizations evolve from traditional data management to next-generation capabilities, they will immediately begin reaping the benefits of modernization. These benefits touch many aspects of the business. But more importantly, they satisfy three major strategic objectives of the modern digital business:
- Empowering digital transformation.
Digital transformation is not optional; you’re either driving it or reacting to it. The digital enterprise recognizes the importance of all data—regardless of origin, format, or content—as a strategic business asset. But with so many sources of data, the number of records organizations must manage can easily reach the billions. Companies need a data management solution that handles this scale, delivering data rigor, accuracy, and security—despite high volume and velocity.
- Self-service for business users.
An intuitive user interface, with a business-friendly user experience, is a great advantage, not just because it’s easy to use, but because it fills an expectation. Today’s app-savvy, mobile-ready workforce is extremely self-motivated and not accustomed to asking IT for favors. Millennials in particular want to solve their own problems using self-service tools that are made for the job. Next-gen MDM lets business users find and explore data to solve their daily challenges.
- Greater agility.
Agility is important. To get it, organizations want easy-to-use tools that don’t require coding, scripts, or waiting weeks for IT help. They also want greater flexibility and modularity in deployment, with the option to spin up data management capabilities rapidly in the cloud. Next-generation MDM offers companies the flexibility to deploy in the cloud, on premise, or in a hybrid setup.
What’s different about next-gen MDM?
MDM’s original charter — to reduce errors and duplicates from data stores — is still alive and well in the overall solution. But changing business needs drive new capabilities, starting with discovering and accessing data, improving it in many ways, and finally delivering it fluidly across the organization in a secure, contextual, and governed manner. Thus, an MDM solution cannot be considered next-generation without delivering these end-to-end capabilities.
To learn more, check out this on-demand webinar on Next-Generation End-to-End MDM Solution.
In part 2 of this series on next-generation MDM, I am diving into the importance of flexible deployment options.








