A solid master data management strategy is key to making effective data-driven decisions
What Is a Master Data Management Strategy?
A master data management strategy is a structured and comprehensive approach to governing and harmonizing an organization’s critical data assets across diverse systems and departments. At its core, master data management (MDM) aims to establish a single, accurate and reliable source of truth for essential data entities, such as customers, products, employees, suppliers and more.
By setting guidelines, processes and technologies for data creation, maintenance and distribution, an MDM strategy helps ensure data consistency, reduces redundancy, enhances data quality and supports compliance. This strategic framework empowers businesses to make informed decisions, drive operational efficiency, power advanced applications like digital twins, and unlock the full potential of their data assets across the departments, teams and business units.
Why a Master Data Management Strategy Is important for the Enterprise Business
Data plays a critical role in the modern enterprise business. In today’s digital landscape, data is generated at an unprecedented pace from various sources — so, ensuring its accuracy, consistency and reliability is paramount. This is where an MDM strategy comes into play.
Let’s delve into five key areas highlighting why MDM is important for deliberate, future-forward organizations:
Modernize Business Processes and Applications
A robust MDM strategy plays a pivotal role in modernizing business processes and applications by providing a consistent, accurate, and centralized source of master data. As organizations update their legacy systems or adopt new technologies, MDM ensures that data inconsistencies and redundancies are minimized, allowing for seamless integration and interoperability. The MDM strategy establishes standardized data models, structures and definitions that can be easily integrated into modern applications, reducing development time and ensuring data accuracy across various systems.
Improve Customer Experiences (CX) and Analytics
MDM directly contributes to improved CX and analytics by offering a unified view of customer data. With accurate and up-to-date customer information, businesses can personalize interactions, identify customer preferences and tailor marketing efforts effectively. Enhanced analytics are possible when data quality is maintained through MDM, leading to more accurate insights and informed decision-making. MDM ensures that customer data is consistent across channels, allowing for a holistic understanding of customer behavior and preferences. See Figure 1 as an example.
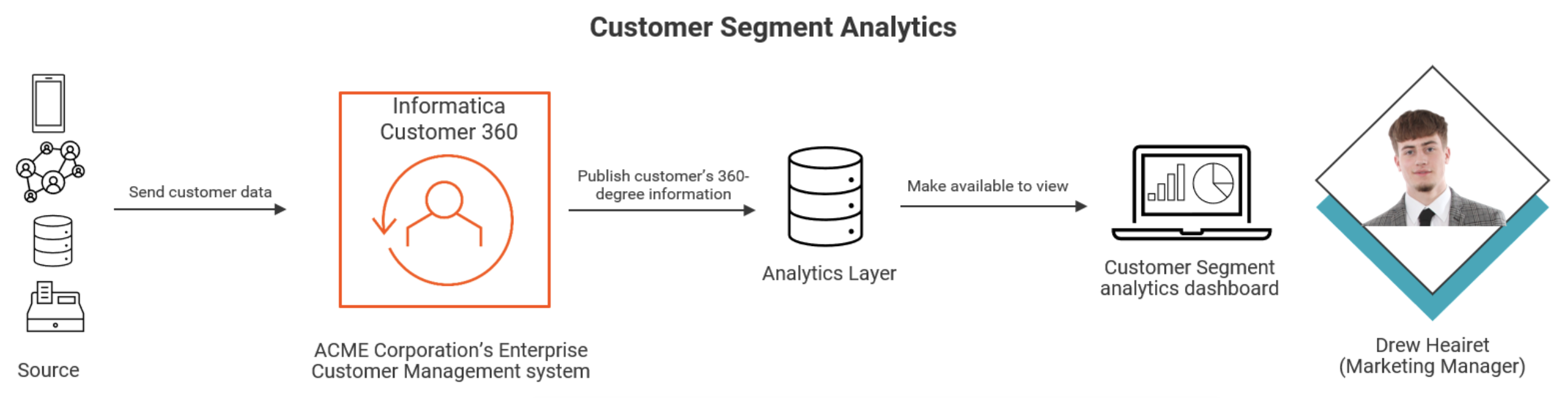
Deliver Engaging Omnichannel Product Experiences
MDM is vital for delivering consistent and engaging omnichannel product experiences. It ensures that product data, including descriptions, specifications and pricing, is accurate and synchronized across all channels. This enables customers to access consistent product information regardless of their chosen platform, leading to better-informed purchasing decisions and a seamless shopping experience.
Improve Supplier Data Management
MDM is integral to operationalizing the supply chain and enhancing supplier data management. By centralizing and standardizing supplier data, organizations can efficiently track and manage their supplier relationships, orders and inventory. MDM enables accurate supplier identification, contact information and compliance data, which is essential for efficient procurement and supply chain operations.
MDM strategy includes management of detailed supplier data
Drive Sustainable Practices and Enable Efficient ESG Reporting
A well-implemented MDM strategy supports sustainable practices and environmental, social, and governance (ESG) reporting. By maintaining accurate data on sustainability metrics, resource usage and environmental impact, organizations can measure and report their efforts accurately. MDM helps ensure that data required for ESG reporting is consistent, reliable and accessible, making it easier to track progress and communicate sustainability initiatives to stakeholders.
Core Capabilities of Master Data Management
There are several core capabilities that must be part of an MDM strategy to drive the many key business imperatives forward in a thoughtful, resource-efficient manner. Aimed at harmonizing and enhancing data assets, these core functions of MDM can collectively help ensure the accuracy, consistency and reliability of unified data. From integrating data from diverse sources to orchestrating data security and privacy measures, MDM functions as a cohesive framework that empowers businesses to bring their data to life, harnessing its full potential.
Capabilities include:
Data Integration: MDM integrates data from various sources and systems across the organization, consolidating it into a unified view. This helps ensure that consistent and accurate data is available for analysis and decision-making.
Data Quality Management: MDM involves processes to improve and maintain the quality of data by identifying and correcting errors, inconsistencies and duplications. High-quality data is essential for reliable business operations and informed decision-making.
Data Governance: MDM establishes data governance policies, standards, and rules to manage data usage, access, security and compliance. This helps ensure that data is managed responsibly and in accordance with regulatory requirements.
Data Modeling and Standardization: MDM defines data models and standards to help ensure uniformity in data structures, formats and definitions. This helps maintain consistency across different systems and departments.
Master Data Creation and Maintenance: MDM enables the creation and ongoing maintenance of master data entities such as customers, products and locations. This helps ensure that these entities remain accurate and up to date.
Data Synchronization: MDM helps ensure that master data is synchronized across various systems and applications, preventing discrepancies and data silos.
Data Access and Distribution: MDM provides mechanisms for controlled and secure access to master data across the organization. It helps ensure that relevant parties can access accurate data for their operational needs.
Change Management: MDM tracks and manages changes to master data over time. This is crucial for maintaining an audit trail and understanding how data evolves.
Metadata Management: MDM maintains metadata associated with master data, helping users understand the context, usage and meaning of the data.
Hierarchy Management: Many entities have hierarchical relationships (e.g., product categories or organizational structures). MDM manages these hierarchies, allowing for accurate reporting and analysis.
Data Lifecycle Management: MDM oversees the complete lifecycle of master data, from creation to archiving or deletion, in compliance with retention policies and regulations.
Data Security and Privacy: MDM enforces security measures to control access to sensitive master data, helping to ensure that only authorized individuals can view and modify it.
Developing a Master Data Management Strategy
Companies should consider the following steps to establish a strong foundation for enterprise-wide data-driven decision-making, operational excellence and sustained success:
- Clear Objectives: Define the specific goals and expected outcomes of the MDM strategy to align efforts and measure success.
- Data Governance Framework: Develop and implement robust data governance policies to ensure data accuracy, security and compliance.
- Technology Solutions: Invest in modernized MDM solutions, with AI-powered automation capabilities that can facilitate data integration, data quality, data management, centralized control and self-service access.
- Change Management: Create a comprehensive change management plan to address resistance and ensure smooth adoption of new processes.
- Cross-Functional Collaboration: Foster collaboration between IT, business units and data stewards to streamline data management efforts.
- Continuous Monitoring and Improvement: Regularly assess the effectiveness of the strategy, refine processes and adapt to evolving data needs.
By addressing these areas and adopting a proactive approach, companies can forge a robust MDM strategy that empowers them to harness the full potential of their data assets and drive informed decision-making across the organization.
Master Data Management in Action
Global biopharmaceutical company Gilead Sciences wanted to improve their MDM, compliance and access to bring data into the hands of employees who need it. They leveraged Informatica MDM solutions to support a data mesh framework. This enabled the company to manage, govern and provide self-service access to data efficiently and cost-effectively across business units. The approach resulted in improved competitive differentiation and data-driven business transformation for faster, more cost-effective drug development, discovery and commercialization.
Insurance brokerage firm Gras Savoye, a subsidiary of Willis Towers Watson, the third-largest brokerage and consulting firm in the world, needed a way to centralize data to better assess the risk of financing fraudulent and illegal activities. They implemented Informatica MDM solutions to create a trusted, comprehensive view of third parties across the organization. This single source of truth allowed the compliance team to spot potential illegal activity.
Master Data Management Resources
- eBook, “4 Steps to a 360-Degree View of Customers, Suppliers and More”
- Webinar, “Meet the Experts: What’s New in Intelligent MDM & 360 Applications”
- Blog, “Cloud MDM — A Phased Approach to Success”
- Video, “Introducing Customer 360 SaaS”
- Data sheet, “Intelligent MDM SaaS”
Visit www.informatica.com/master-data-management for more information on Informatica’s MDM solutions.





