Simplify Data Integration of NoSQL Databases for a Unified View of Valuable Insights

Traditionally when a developer planned to build a user application, they relied on relational databases for storing structured data in a systematic way. It was expected that the underlying database would maintain integrity and reliability of the stored data. However, today we are seeing a new breed of applications that can stream customized content online or provide a real-time online shopping experience with other services.
With such diverse user applications, data cannot remain structured and natively fit into predefined relational database schemas. These applications are generating semi-structured and unstructured data at scale. It’s challenging to integrate mixed data types and convert them into a format that can be easily accessed and interpreted for valuable insights.
Plus, many developers don’t know how to standardize and integrate data from both NoSQL databases and relational databases. Combining it is complex and requires advanced transformation capabilities. But not combining it can cause shortsighted business decisions. The ability to merge data from structured and unstructured sources in a single integration pipeline can help resolve these issues. It can also save time and provide a unified view of data to inform business insights. Let’s explore this in detail.
How Customers are Leveraging NoSQL Databases Today
Over the last couple of years, we have seen our customers move to cloud NoSQL databases like Amazon DynamoDB, MongoDB Atlas and Azure Cosmos DB. Our customers are also using in-memory databases like Redis or Elasticsearch for use cases where a quick search of reference data is required.
In today’s cloud-first world, in-memory and NoSQL databases are handling data loads at scale. For example, Amazon Prime has modernized their backend database to DynamoDB for their growing business data. Other open-source versions are also gaining momentum in the cloud developer society.
The benefits of using NoSQL databases include the ability to:
- Efficiently handle unstructured or semi-structured data
- Process large volumes of data at scale with its scale-out architecture
- Eliminate the need to maintain schematic of data in their applications
We’re seeing a consistent rise in popularity of NoSQL databases with virtually any cloud-first, cloud-native company across the world. This creates a unique deployment architecture where NoSQL databases or in-memory databases like Redis or Elasticsearch sit along with modern cloud data warehouses and data lakes. The NoSQL databases, when used for transactional storage, hold valuable data and become an extremely important source for modern analytics data warehouse deployment.
Common Use Cases for NoSQL Databases
Based on discussions with our enterprise cloud customers who have adopted NoSQL/in-memory databases, their common use cases include:
- Extracting data out of NoSQL sources and pushing it to a cloud data warehouse for doing further data analytics
- Building a mirror image of their master NoSQL databases to offload some of the non-critical workloads to an alternate site
- Migrating from legacy on-premises NoSQL databases to cloud NoSQL databases
How Informatica’s Data Integration Capabilities Support NoSQL Databases
Informatica Cloud Data Integration, a service of our Informatica Intelligent Data Management Cloud™ (IDMC), helps enterprises deploy their hybrid integration pipeline and work seamlessly across on-premises and cloud endpoints.
The Informatica Cloud Data Integration service advanced mode now supports NoSQL databases as endpoints for advanced mode execution, which could be an ideal solution for such deployments.
It supports data integration workloads for NoSQL and in-memory cloud databases, including:
- MongoDB Atlas and on-premises MongoDB
- Amazon DynamoDB
- Microsoft Azure Cosmos DB
- Redis
- Elasticsearch
This enables you to define complex and hybrid workloads using our advanced mode mappings. You can now read and write data from NoSQL and unstructured databases and handle scenarios as described below.
- Moving nested or hierarchical data to a structured relational target. The Informatica Cloud Data Integration service advanced mode can read hierarchical data from a NoSQL source and parse it. It does this by understanding its structure, which can be further transformed by using our rich set of transformations and then ingesting it to a target cloud data warehouse. This includes Amazon Redshift, Snowflake, Databricks Delta and Google BigQuery — all of which are commonly used for complex analytics use cases.
In Figure 1, you can see how our NoSQL connector can read nested data and project it to our mapping designer so developers can easily transform it in the desired output.
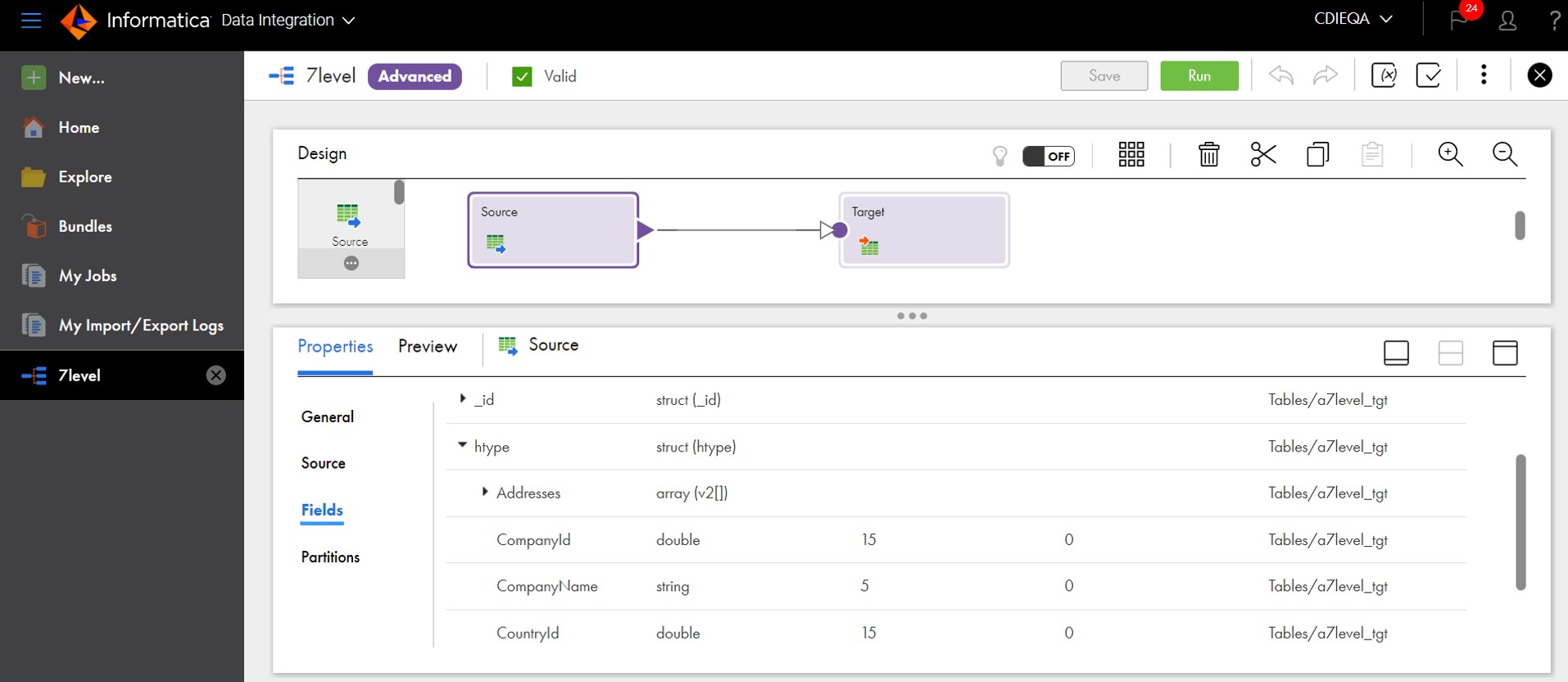
- Reading structured relational data to loading to NoSQL databases. The Informatica Cloud Data Integration service advanced mode capabilities can also build a hierarchy from incoming flat data sources and load it to NoSQL targets. In Figure 2, you can see how incoming data from flat sources can be designed as hierarchical output. In addition, this also allows you to have flexibility to define the nested array and their datatypes. Enterprises increasingly want to execute reverse ETL workloads. They are primarily reading from analytics data warehouses and ingesting insights back to transactional applications, which are running on NoSQL databases. The Informatica Cloud Data Integration service makes this possible.
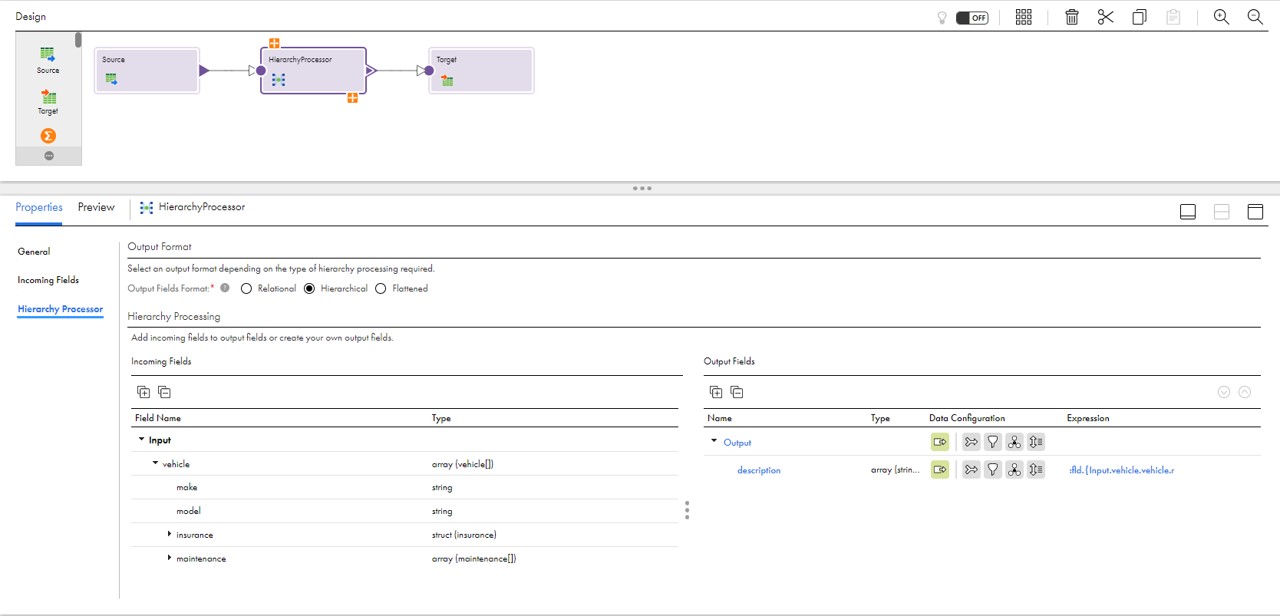
- Execution at scale on Spark clusters. You can also leverage our Spark elastic cluster to execute NoSQL workloads at scale. In addition, the autoscaling feature eliminates the requirement of running static clusters 24/7. This significantly reduces operational costs on the public cloud without compromising the performance of the data pipeline. Learn more about the Informatica Cloud Data Integration Elastic service cluster and best practices here.
Next Steps
If you are working with unstructured data and want to efficiently manage data integration workloads, the Informatica Cloud Data Integration service can help. Start a free 30-day trial now.








