Table of Contents
- What Is the EU AI Act?
- Why Is the EU AI Act Important?
- How Does the EU AI Act Define Risk?
- The Global Impact of the EU AI Act
- Preparing for the EU AI Act
- AI and Compliance: Data Management Takes Main Stage
- Integrated Data Management: The Key to Driving Business Impact
- Informatica Customers: Tangible Business Benefits Already
- Informatica Aims to Ensure AI Compliance and Boost Performance
What Is the EU AI Act?
The European Union Artificial Intelligence Act, also known as the EU AI Act, is a comprehensive legal framework proposed by the European Union (EU) for AI regulation. Its aim is to ensure the safety and fundamental rights of citizens and businesses. This Act classifies AI systems based on their associated risks and implements specific rules for each category, fostering the use of AI that is lawful, ethical and robust across the EU.
The EU AI Act will become law between May - July 2024 1 (see timelines to adoption later), setting a global benchmark for AI regulation. The Act is intended to ensure that AI systems are:
- Safe, transparent and traceable
- Non-discriminatory
- Environmentally friendly
- Respectful of existing privacy laws and people’s fundamental rights
Why Is the EU AI Act Important?
The Act establishes rules for creating and using AI in the EU, aiming to foster innovation and curb potentially harmful uses. As it states, “The AI Act aims to provide AI developers and deployers with clear requirements and obligations regarding specific uses of AI. At the same time, the regulation seeks to reduce administrative and financial burdens for business, in particular, small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs).” 2
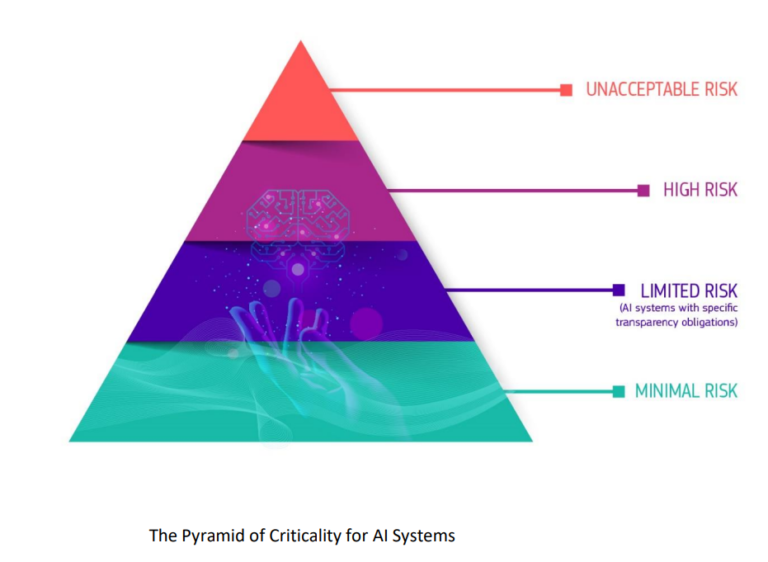
Figure 1: The regulatory framework defines four levels of risk for AI systems.
How Does the EU AI Act Define Risk?
The Act categorizes AI systems based on their risk to rights and safety.3 As illustrated in Figure 1, the Act defines the following:
Unacceptable risks, such as social scoring by governments, will be banned.
High-risk systems, including those used in critical infrastructures, law enforcement or procedures affecting workers' rights, must comply with strict requirements before deployment. This includes rigorous testing, transparency obligations and the provision of high-quality data sets that avoid discrimination. A prevalent example is real-time remote biometric identification systems, like facial recognition.
AI systems deemed low or minimal risk, such as the use of chatbots, will have lighter regulatory burdens; for example, AI-generated text will have to be labeled as such and AI-enabled video games or spam filters will have free use, encouraging innovation, while ensuring that systems are trustworthy.
The Global Impact of the EU AI Act
More Regulations in the Works
The EU AI Act is leading the way in publishing AI regulatory controls, but similar acts are being developed in other parts of the world, like the Singapore Model AI Governance Framework,4 the USA Executive Order on AI5 and others. The extensive global influence of the EU AI Act extends beyond Europe's borders, affecting organizations worldwide through its comprehensive approach to AI governance.
While the EU AI Act has a broader and more detailed approach, targeting both public and private sector AI applications, the Executive Order in the U.S. outlines a strategic plan and set of principles (see Informatica take here). Moreover, the Singapore Model AI Governance Framework is a voluntary scheme offering detailed and extensive suggestions on how organizations can ethically use AI. They all, however, demonstrate the increasing importance of responsible AI governance and the interconnected nature of worldwide regulatory control.
The Global Marketplace and the EU AI Act
Understanding how to manage the organizational requirements of the EU AI Act naturally extends into operating in the marketplace with customers and competitors alike. As such, the impact of this new legislation will be felt beyond EU boundaries due to the global nature of the digital economy, as it purports: The aim of the new rules is to foster trustworthy AI in Europe and beyond by ensuring that AI systems respect fundamental rights, safety, and ethical principles and by addressing risks of very powerful and impactful AI models.6
Therefore, the EU AI Act can compel non-EU countries and companies to evaluate and potentially adjust their AI strategies and services if they wish to operate in the EU market, potentially standardizing regulations across regions, enabling some organizations to gain competitive advantage through better alignment on compliance and operating partner relationships with greater harmonization. These far-reaching implications reaffirm the importance of understanding and engaging with international regulations in an increasingly complex world.
Preparing for the EU AI Act
Finally, as stated in the EU directive, the AI Act will enter into force 20 days after its publication in the Official Journal due between May - July 2024 and fully applicable two years later, with some exceptions: prohibitions will take effect after six months, the governance rules and the obligations for general-purpose AI models become applicable after 12 months and the rules for AI systems - embedded into regulated products - will apply after 36 months. 7
This act is at the vanguard of AI regulations being developed in different regions. The challenge of being ready for these regulations is upon us all.
It can be a bewildering prospect for modern enterprises to understand how to shape complex and sometimes abstract organizational and business change, and the EU AI Act is accelerating the pace of this change. Informatica understands these challenges and what CDOs are struggling with; its Intelligent Data Management Cloud™(IDMC) platform and data management solutions provide a powerful, automation-driven, end-to-end ecosystem to support your AI/ML requirements.
AI and Compliance: Data Management Takes Main Stage
Nearly nine in ten (87%) analytics and IT leaders agree that advances in AI make data management the highest priority.8
Transformational AI has quickly become pervasive as we enter the third wave of digital transformation in the past decade, powered by AI and data. Fundamentally, AI systems depend on data — the quality and quantity ingested directly impact their effectiveness. Essentially, data fuels AI, enabling learning, adaptation and decision-making within the digital ecosystem.9
Data Governance and AI
Having high-quality, reliable data is a cornerstone of effective decision-making in any organization; thus, robust data governance becomes essential, ensuring the availability, consistency, integrity and security of valuable data across the enterprise. Without good quality data, organizations risk deploying AI systems that are inaccurate, biased and potentially non-compliant with regulation. Conversely, by ensuring high-quality data, organizations can realize the full potential of AI, harnessing its power for precise, unbiased and trusted outcomes. Data governance had its roots in protecting sensitive data from abuse and providing reporting transparency; this critical capability has further evolved into data empowerment, driving business performance.
Now, it’s not just about reducing risks of misuse and manipulation, data governance can support the democratization of data, so the right people get the right data to be more productive. For example, this can involve reducing administrative burdens, often caused by friction during data sharing and delivery.
Navigating this new era requires a modern approach to data and AI governance, which can be encapsulated within:
1. Risk and Compliance – Enhancing data transparency, prioritizing data privacy and mitigating bias and risk in AI. Data governance can apply automated controls to ensure that only the right people gain access, thus preventing misuse or risk exposure that could lead to abuses.
2. Data Sharing and Democratization – Ensuring the discoverability, trustworthiness and accessibility of data assets to all levels of data consumers and promoting data democratization across the organization. Data governance entails understanding the available data by finding, classifying and curating data types and delivering them for use.
3. Intelligent Data Observability – Allowing companies to monitor the use of data for data quality-related issues, improving data flow and helping to ensure data security, integrity and transparency. Data governance aids in the scalability of your digital business, effectively handling increases in data volume, user numbers and requests for data access.
Data Governance and AI in Action: How a Global Pharma Company Drives Efficiencies and Compliance
A prominent biopharmaceutical company headquartered in the U.S. with significant operations across the EU underwent a transformative shift in its data management architecture. Transitioning from a rigid, monolithic setup to a more agile and business-focused decentralized data mesh architecture, the company aimed to enhance its data management capabilities to support its strategic goal of delivering 10+ transformative therapies to patients by 2030.
The strategic shift in data management architecture closely aligns with the principles outlined in the EU AI Act. Transitioning to a decentralized architecture has not only enhanced data management capabilities but also positioned the company to comply with its stringent requirements.
The Act's focus on fostering innovation while ensuring AI systems are safe, transparent and respectful of fundamental rights resonates with the commitment to delivering transformative therapies to patients. The company's adoption of the Informatica Intelligent Data Management Cloud™ (IDMC), coupled with its embrace of data mesh principles, underscores the importance of robust data management strategies in achieving compliance with the EU AI Act and maintaining a competitive edge in the pharmaceutical industry.
Embracing a Single Source of Truth for EU AI Act Compliance
In the context of the EU AI Act, establishing a single source of truth for data becomes not just a best practice but a regulatory imperative to ensure data is traceable. This approach supports collaboration and effective data management, which is crucial for ensuring compliance with the Act's stringent governance requirements. By consolidating all data management activities into one platform, organizations can more readily define clear responsibilities for data, policies and processes. This approach streamlines workflows and promotes a consistent approach to metadata management, making it easier to apply and automate data protection and privacy measures, as mandated by the EU AI Act.
A centralized governance platform also provides policy owners a comprehensive view of how data interacts with various processes, technologies and stakeholders. This visibility enables them to refine or adapt policies in line with the evolving regulatory landscape. For analysts, a single source of truth allows them to track the lineage of data, ensuring the accuracy and reliability of insights generated from AI-managed big data. This capability is critical under the EU AI Act, which emphasizes transparency and accountability in responsible AI decision-making processes.
By embracing a single source of truth for data management, organizations can enhance their operational efficiency and ensure compliance with the EU AI Act's governance requirements, ultimately fostering trust and transparency in AI-driven decision-making processes.
Integrated Data Management: The Key to Driving Business Impact
The current reality for most organizations is, of course, markedly different. Informatica’s 2024 CDO survey highlights that 58% of respondents already manage more than five tools just to wrangle the 1000-plus data sources 41% are utilizing. As the volume of data and data quality consumers exacerbate the strain placed on data leaders, the need for a single consolidated solution to manage all this data becomes abundantly clear. Simplifying the governance process must be a key objective for chief data officers (CDOs), particularly as they navigate an ever-expanding portfolio of responsibilities and duties.
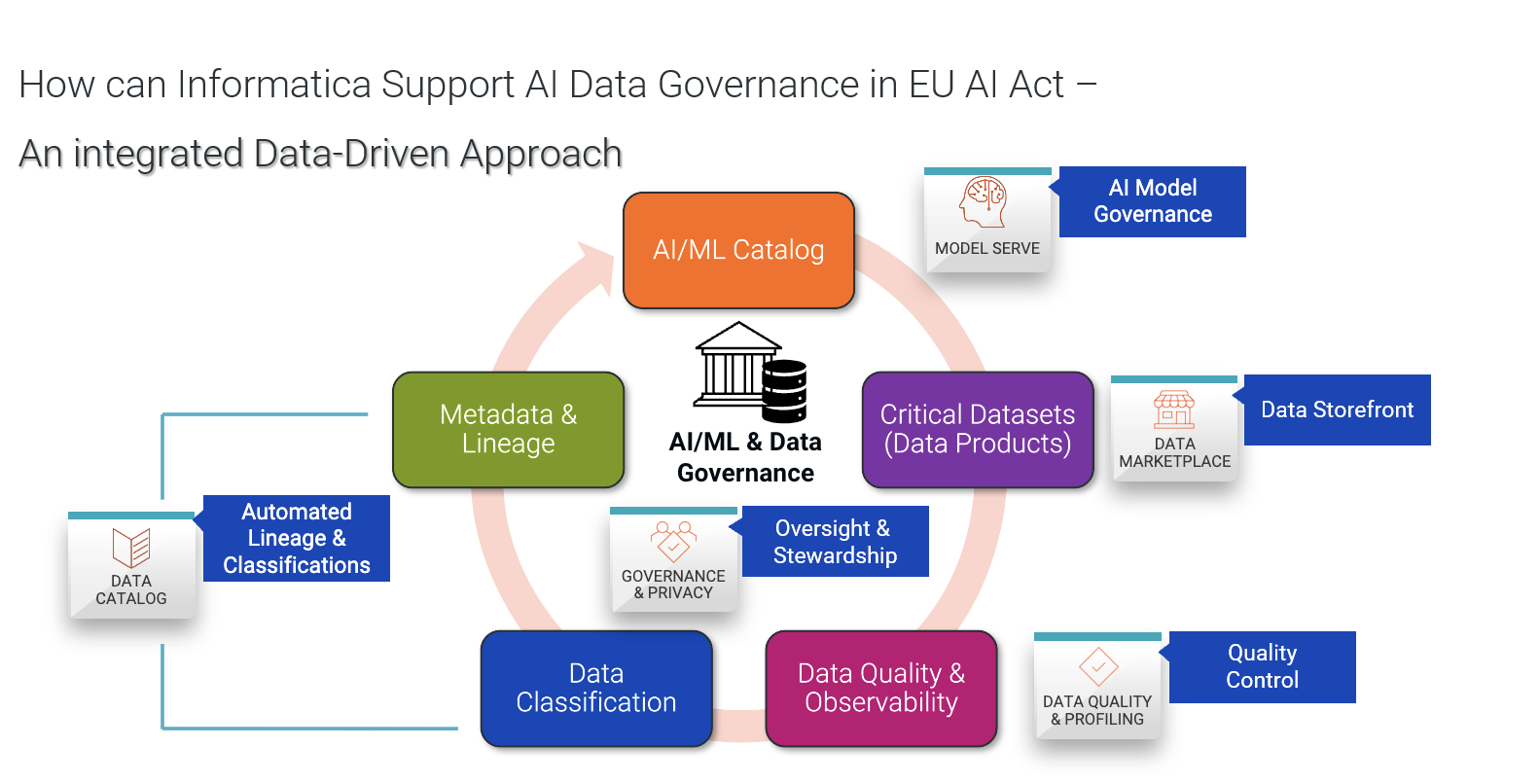
Figure 2: Informatica platform offering an integrated solution to data governance.
To alleviate the CDO’s burden of growing governance responsibilities, the Informatica Intelligent Data Management Cloud™ (IDMC) offers a unified, AI-powered solution that uses predictive, automated data intelligence to deliver reliable data for intelligent decision-making. As depicted in Figure 2, organizations can automate various aspects of data management — such as data cataloging and lineage, data quality, data observability, master data management (MDM), data security and privacy, and data sharing — by leveraging Informatica’s metadata-driven AI engine, CLAIRE® (cloud-scale, AI-powered real-time engine). These facets are vital in enabling organizations to support ethical, fair, transparent and responsible AI systems.
“On Artificial Intelligence, trust is a must, not a nice to have.”
-Margrethe Vestager, Executive Vice-President for a Europe fit for the Digital Age10
Improving AI Readiness
CDOs and other data leaders understand that businesses are only ready to adopt AI if data is also reliable and ready for AI. Increasingly, improving AI readiness is becoming the most common metric for measuring data strategy effectiveness. This is a business imperative, not just a data governance issue, ensuring customers are confident interacting with organizations in a trustworthy way.
Informatica’s CDO Insights 2024 Survey confirms that almost half of the CDOs surveyed (48%) would consider upskilling or reskilling their staff on AI and machine learning. Organizations grapple with how to build trust and efficacy through a better AI strategy within their organization and with their customers. In addition, over 75% of consumers are concerned about misinformation from AI.11
There are clear learnings and confidence that can be built across business operations. These technical roadblocks to AI adoption are coupled with business obstacles such as a lack of support from business leadership (45%), inability to justify ROI for budget (45%) and lack of cooperation/alignment across business units (44%).12
While there are significant challenges to ensuring organizations are fit to take advantage of AI, the prize is demonstrably large: Generative AI could add the equivalent of $2.6 trillion to $4.4 trillion13 in annual economic opportunities globally, principally in areas such as R&D, manufacturing, sales and marketing and customer operations.
Informatica Customers: Tangible Business Benefits Already
Informatica’s customers across the globe have already witnessed significant growth in business performance from adopting its AI-powered solutions:
Banco ABC Brasil: By migrating to a cloud data lake, Banco ABC Brasil improved data self-service capabilities, scaled data analysis, reduced costs, and monetized its data assets. With 70% of the credit application process being automated, the bank can offer a better customer experience.
BMC Software adopted IDMC to make cost savings of 40% (you can read more customer success stories here).
Tangible business benefits have been realized across many industries and regions worldwide, with new AI-powered initiatives being developed every day.
Saudi Airlines have just announced a travel companion which is one of the first ChatGPT4 bases for personal assistants in the airlines globally, and IDMC is the bridge for this initiative by bringing data AI to life.
Informatica Aims to Ensure AI Compliance and Boost Performance
Informatica’s vision for data management is one of unification and empowerment. It encompasses a foundation enabling self-serve access to valid, trustworthy data, (with) AI-infused tools amplifying productivity and enriching user experiences.14 (You can read more about Informatica’s vision in this blog article Designing a Principled Product Strategy for AI-Powered Data Management).
Informatica Intelligent Data Management Cloud (IDMC) plays a central role in de-risking AI initiatives and enhancing compliance with regulations like the EU AI Act. The comprehensive solution offers data governance, privacy control, data quality improvement and AI-powered data cataloging to ensure transparency, reliability and integrity of data. This is all done through a data management platform that is multi-vendor, multi-cloud (including AWS, Azure and Google) and hybrid, supporting on-premises and cloud-based data storage and management. Through automated data management tasks and seamless data integration, IDMC increases operational efficiency and creates a single source of truth.
By ensuring high-quality and well-governed data feeds into AI models, IDMC not only enhances their accuracy, reliability and fairness, but also facilitates compliance with stringent regulations. Thus, it aids organizations in building AI systems that are transparent and accountable, respect privacy and support data protection rights. It also crucially helps drive improved business performance through better data governance every step of the way.
Next Steps
For more insight on ways Informatica helps organizations with their data governance and AI strategy, visit us at www.informatica.com/data-governance.
2https://digital-strategy.ec.europa.eu/en/policies/regulatory-framework-ai
3https://www.artificial-intelligence-act.com/#:~:text='Artificial%20intelligence%20system'%20(AI,logic%2D%20and%20knowledge%20based%20approaches%2C
4https://www.pdpc.gov.sg/help-and-resources/2020/01/model-ai-governance-framework
5https://www.whitehouse.gov/briefing-room/presidential-actions/2023/10/30/executive-order-on-the-safe-secure-and-trustworthy-development-and-use-of-artificial-intelligence/
6https://digital-strategy.ec.europa.eu/en/policies/regulatory-framework-ai
7https://digital-strategy.ec.europa.eu/en/policies/regulatory-framework-ai
8Salesforce State of Data and Analytics report
9https://www.forbes.com/sites/forbestechcouncil/2023/10/05/ai-needs-data-more-than-data-needs-ai/
10https://digital-strategy.ec.europa.eu/en/news/europe-fit-digital-age-commission-proposes-new-rules-and-actions-excellence-and-trust-artificial#:~:text=Margrethe%20Vestager%2C%20Executive%20Vice-
11https://spectrum.ieee.org/state-of-ai-2023
12CDO Insights 2024: Charting a Course to AI Readiness
14Designing a Principled Product Strategy for AI-Powered Data Management





