Data Lake and Data Warehouse Modernization in the Cloud – 3 Steps to Avoid Past Mistakes
Realize the Benefits of Cloud with the Three-Pillar Framework

Tetris is a fun game that we’ve all played it at some point or the other. As you progress in the game, you make mistakes and learn from them. Then you get better and score higher. It’s the same idea with the cloud data management and data lake and data warehouse modernization. Ok, now it’s not so trivial! But the idea is the same: not to repeat past mistakes from on-premises data lakes and data warehouses. What do I mean by past mistakes? Let’s first take a quick look at the data landscape for AI and big data analytics.
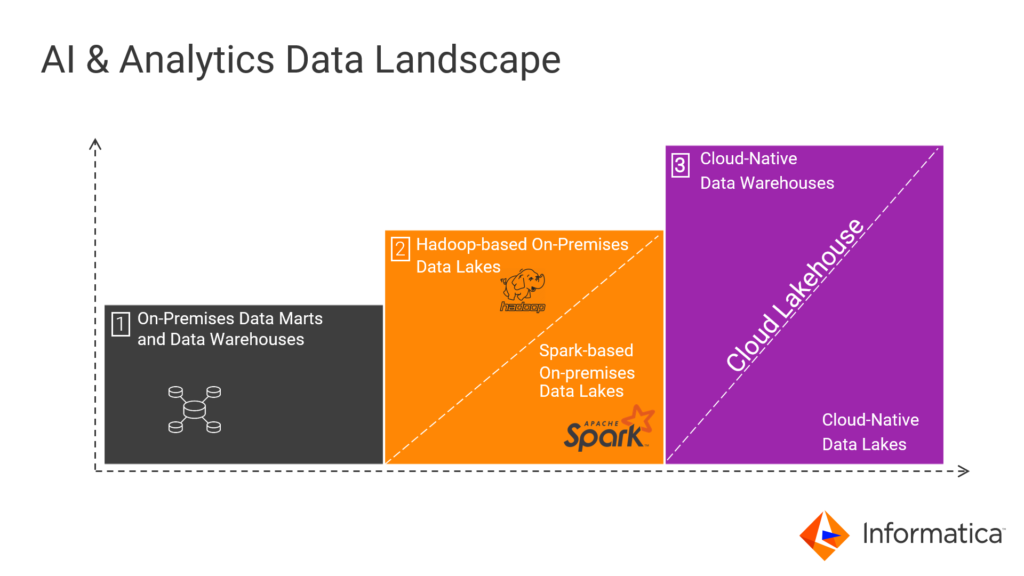
The AI and Big Data Analytics Landscape
As you look at the evolution of the landscape for AI and big data analytics, first there were data marts and then there were data warehouses on-premises. These made business intelligence (BI), reporting, and dashboards possible. The evolution continued with data lakes that were Hadoop-based, and continued with innovation toward Spark-based data lakes. This paved the way for faster analytics and insights. Due to operational complexity, maintenance, and cost considerations, all of this moved to the cloud.
According to Gartner, by 2023, 75% of all databases will be on a cloud platform, reducing the DBMS vendor landscape and increasing complexity for data governance and integration.[1]
Now we have cloud-native data lakes and data warehouses. In fact, cloud data warehouses and data lakes are coming together in a unified architecture known as a cloud lakehouse. A lakehouse offers you a view into not only what happened and what is happening, but also what is going to happen. Today you can solve for a number of use cases: fraud detection, risk reduction, next-best action, supply chain optimization, just to name a few. All delivered with the promise of the cloud: agility, scalability, and lower costs.
Data Pipeline Déjà Vu!
Now let’s look at potential mistakes. As you move to the cloud, hand coding appears like an easy option to build your data pipeline. A hand-coded data pipeline means you’re paying people. But people don’t scale – they’re valuable resources. Hand coding is expensive, its price increases as complexity increases. Finally, hand coding is inefficient if you run into issues and need to recode, it gets even worse if a data engineer leaves your company. These are some of the key mistakes of the past. Feels like déjà vu, isn’t it? Data management in the cloud is an opportunity, but repeating past mistakes is not a strategy. Fortunately, there’s a strategy for data management in the cloud.
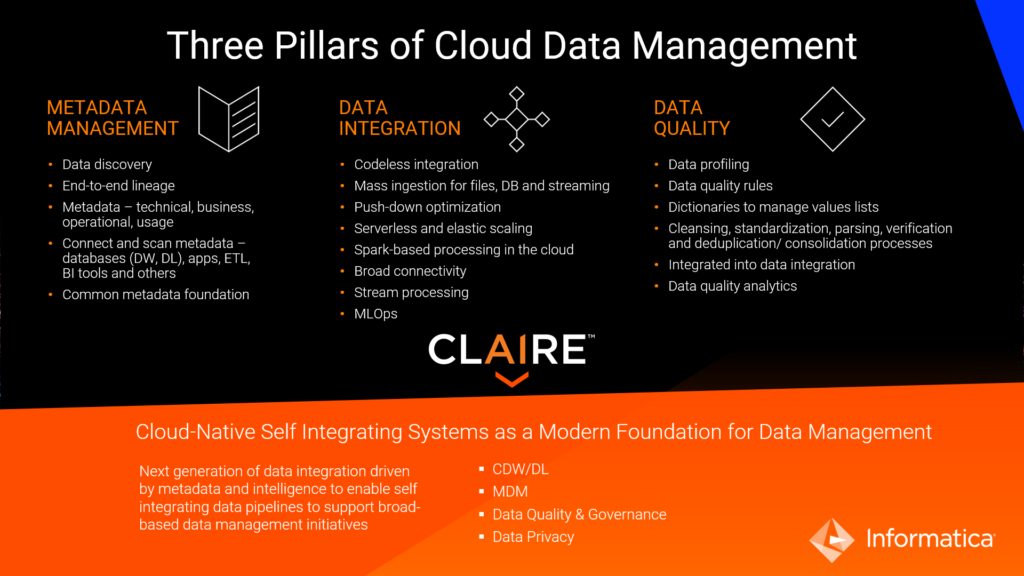
Three Pillars of Cloud Data Management
When we look at our customers, we see broadly three key pillars of cloud data management to drive successful outcomes for big data analytics and AI projects. By addressing these three pillars, you can avoid the data management mistakes of the past.
- Metadata Management. First, you need metadata management to effectively catalog, discover, and understand how data is moving through your organization. Informatica Enterprise Data Catalog (EDC) can help you discover and inventory data assets across your organization.
- Data Integration. Next you need data integration. Data integration is more than simple ingestion, a best-of-breed solution supports all data ingestion and integration patterns. Mass ingestion of files, IoT streaming data, and database initial and incremental loads are key requirements to hydrate your data lake. Look for ETL/ELT and pushdown optimization to process data once it’s in the cloud, ideally doing this in a serverless elastic scaling runtime. You also need the broadest connectivity across clouds, SaaS, and on-premises applications. Informatica Intelligent Cloud Services Cloud Mass Ingestion (CMI) and Cloud Data Integration (CDI) offer zero-code, wizard-based user interfaces that help you avoid hand coding through metadata-driven artificial intelligence and automation.
- Data Quality. The third pillar, data quality, enables you to deliver trusted data through comprehensive profiling, data quality rule generation, dictionaries, and more. Informatica Cloud Data Quality (CDQ) helps you quickly identify, fix, and monitor data quality problems in your cloud and on-premises business applications.
Lastly, to drive intelligent automation for each of the above three pillars of data management you need an AI foundation. In other words, data needs AI. The Informatica AI engine CLAIRE leverages industry-leading metadata capabilities to accelerate and automate the data management functions. This framework not only helps avoid past mistakes of data management but also helps you navigate to Data 4.0, the soul of digital transformation.
Learn More
- Catch Gartner Distinguished Vice President Analyst Mark Beyer’s talk at the Intelligent Data Summit for Cloud Data Warehouses, Data Lakes, and Lakehouses
- Catch the webinar Comparative Costs and Uses of Data Management for Cloud for best practices to avoid cloud data management mistakes of the past
- Read the executive brief Intelligent Cloud Lakehouse Data Management for Cloud Analytics
[1] Gartner, “Data Management in the Cloud is not an Opportunity to Repeat old Mistakes,” Mark Beyer, 2 June 2020








