Three Ways Master Data Management Improves Digital Commerce
Last Published: Mar 17, 2025 |

Digital commerce where anyone can find, research, and buy online using their device of preference is now the primary way of doing business. While business-to-business (B2B) companies had typically lagged behind business-to-consumer (B2C) companies, the COVID-19 pandemic was a wake-up call that dramatically accelerated the adoption of digital channels. And consumer brands that traditionally sold through retailers, online marketplaces, and distributors launched new direct-to-consumer programs during the pandemic.
While consumers will resume visiting as they reopen, the frequency is unlikely to reach levels seen before the pandemic for some time. Even older consumers have acclimated to digital channels and interactions, and many digital behaviors are likely to persist across demographics and regions. For example, a McKinsey survey found 40 to 65 percent of consumers intend to continue using contactless services, such as buy online and curbside pickup. [1]
Before I describe the three ways master data management (MDM) improves digital commerce, let’s level set on a definition of digital commerce, and metrics for measuring its success.
What Is Digital Commerce?
According to Gartner, “Digital commerce enables customers to purchase goods and services through an interactive and self-service experience. It includes the people, processes, and technologies to execute the offering of development content, analytics, promotion, pricing, customer acquisition and retention, and customer experience at all touchpoints throughout the customer buying journey.” [2]
Measuring Digital Commerce Success
The first thing that probably enters your mind when you hear digital commerce is revenue generation. While revenue generation is an important aspect of digital commerce, I would argue that cost management is equally important because you want to measure both revenue and expenses, so you can determine how effective and efficient you are at turning sales into profit. And it is important to manage not just how much money is coming in from sales and how much money is going out in expenses, but also cash flow, which is the timing of when cash comes in and when it goes out. A problem with either profit or cash flow can make it difficult for a company to stay in business.
Three Ways Master Data Management Improves Digital Commerce
In the 2021 Magic Quadrant for Master Data Management Solutions [3], “Gartner defines master data management (MDM) as a technology-enabled business discipline in which business and IT work together to ensure the uniformity, accuracy, stewardship, governance, semantic consistency, and accountability of an enterprise’s official shared master data assets.” Using revenue generation, cost management, and cash flow as our measures for digital commerce success, let’s see how master data management helps improve each. The examples below are representative but not exhaustive.
Master data management helps improve digital commerce by increasing the accuracy and consistency of master data across sources, which increases the accuracy of reporting on the current state of performance, analysis on the reasons for the current state, and modeling scenarios for improvement. MDM also helps in the operational execution of plans to address issues and capitalize on opportunities.
From a master data management perspective, it’s not uncommon for people to focus primarily on Product Information Management (PIM) when they discuss digital commerce. While product is a critical master data domain, digital commerce is a multidomain, multidisciplinary practice that requires collaboration across business functions, each having specific master data requirements. Organizations that underestimate the breadth of master data management capabilities needed will likely struggle in effectively and efficiently managing the entire value chain of digital commerce.

1. Improving Digital Commerce Revenue Generation with Master Data Management
There was a dramatic shift in the drivers of purchasing decisions and a disruption to brand loyalty in 2020 as consumers tried different brands in new digital channels that they may not have otherwise. Initially, convenience and value were the primary catalysts for brand switching. However, consumers are also seeking goods and services from brands that align with their values. For example, Unilever, Informatica’s Intelligent Disruptor of the Year in 2021, sees its sustainable living brands consistently outperform in terms of revenue growth and profitability.
Master data management can help you improve identification and understanding of changing lifestyle or consumer mindset trends, so marketing can be tailored by audience and region, delivering relevant messages through preferred channels. Creating comprehensive customer profiles — including demographic, geographic, sentiment, household, and channel preference information — improves customer segmentation and the accuracy of propensity-to-buy modeling. The increase in accuracy of analysis, in turn, improves the response rates to personalized marketing offers.
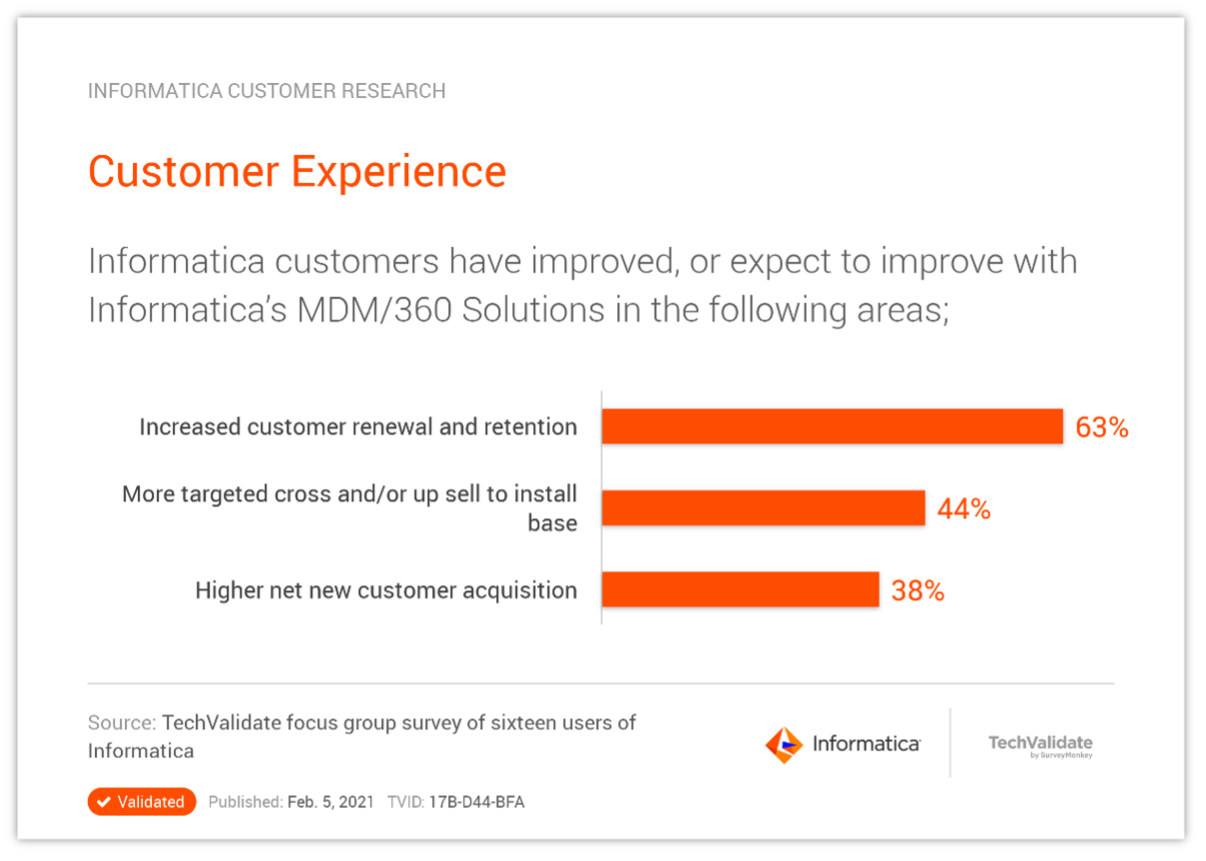
For example, a large beauty retailer increased wallet share and lifetime value by implementing master data management to improve the quality of data used in machine learning models. With more accurate predictions about what customers want and when, they can increase sales with increasingly relevant product suggestions and replenishment reminders timed to personal history. increase sales with increasingly relevant product suggestions and replenishment reminders timed to personal history.
When customers visit the retailer’s ecommerce site or use its popular mobile app, they’re greeted by name and presented with offers that are most likely to compel action. Virtual beauty advisors leverage the customer data to deliver product simulations using the mobile app, allowing customers to “apply” makeup to see what colors they like. With better data for analytics, the retailer can now target customers based on new insights for individual and household demographics, preferences, and segmentation.
Master data management can also help you improve execution of the insights generated from analysis. Product variants are an important part of driving revenue through different channels to audiences with different purchasing criteria and values. While the product itself is the same, there are variants of product descriptions, labeling, and packaging that emphasize attributes important to the audience. For example, Unilever just announced the world’s first paper-based laundry detergent bottle, which is part of its strategy around sustainable packaging to address environmental issues that people care about.
Master data management can help you:
- Speed the creation of information for product variants
- Get the information into the appropriate channels
- Ensure the right variant information is used for marketing to specific segments
One Informatica customer increased the productivity of creating information for product variants by 83%, which, in turn, helped them accelerate time-to-market and improve execution of turning insights into revenue-generating activities.
2. Improving Digital Commerce Cost Management with Master Data Management
Cost improvement opportunities exist across the entire value chain of digital commerce including:
- Customer acquisition costs
- Procurement costs
- Manufacturing costs
- Warehousing costs
- Transportation costs
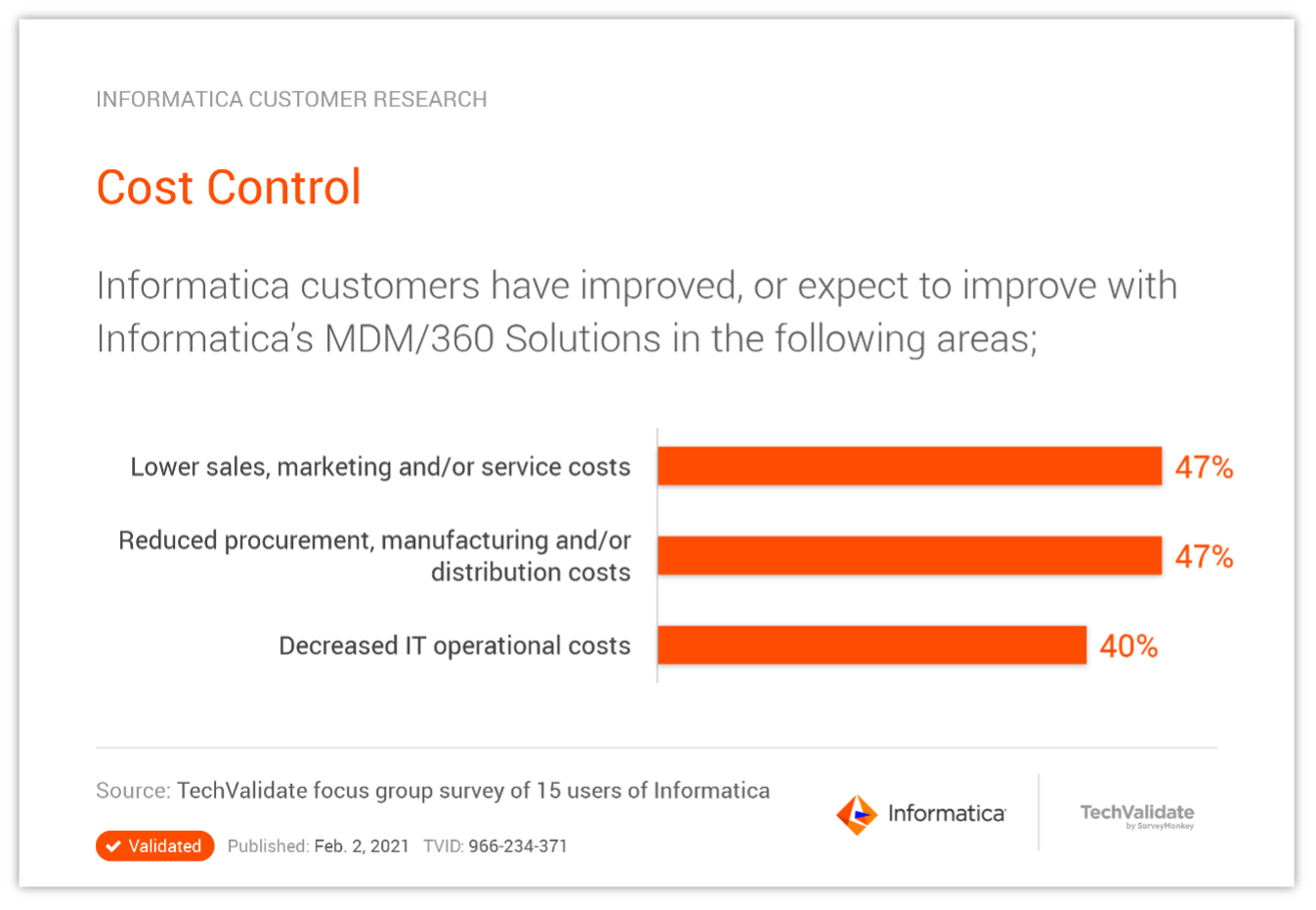
However, without a holistic view across the digital commerce value chain, each functional area of the business pursues its own interests, which may conflict with the interests of other business functions. Master data management helps increase the precision of analysis of the interrelationship between functions and the levers for cross-functional optimization.
For example, in the last section, I talked about the creation of product variants to appeal to audiences with different purchasing criteria and values. Each of the product variants is a different stock-keeping unit (SKU). And while sales want as many SKUs as possible to increase market share, SKU proliferation makes it difficult to forecast accurately, control procurement and manufacturing costs, and manage warehouse inventory levels.
Master data management is critical to determining the total value of each SKU, so you strike the right balance between market opportunities and operating costs. Portfolio optimization requires accurate SKU information about a wide range of costs, including bill of materials, labor, and cost to serve, as well as SKU information about sales like price, turnover velocity, and channel performance. This analysis helps guide SKU rationalization by portfolio segment based on target margin levels, consumer success drivers, and product cost drivers to optimize overall portfolio performance. Portfolio optimization can lead to cost reductions in the 10 to 20% range, and margin improvements between 2 to 6%. [4]
Optimizing order fulfillment is another opportunity for cost improvement. The pick-and-pack process typically constitutes most of the time and cost associated with order fulfillment. The growth of ecommerce in 2020 created an even stronger need for efficient fulfillment solutions. The smaller unit picks, mixed orders, and high-speed delivery make fulfillment challenging.

Kroger, another Informatica Innovation Award Winner, saw 116% growth year on year in digital commerce revenue. It has committed to further doubling its digital business going forward. To position itself as a leading ecommerce company, Kroger knows that fast, efficient, and cost-effective last-mile delivery is critical. It is implementing a customer fulfillment center model that uses robots and algorithms to control the pick-and-pack process. Items are intelligently packed with fragile items on top, bags are evenly weighted, and each order is optimized to fit into the lowest number of bags, reducing waste. Master data such as item location, weight, dimensions, and packing requirements are critical to the success of this automation.
3. Improving Digital Commerce Cash Flow with Master Data Management
Assessing the amounts and timing of cash flows, along with where they originate and where they go, is essential for assessing a company’s liquidity and overall financial performance. Even profitable companies can fail if their operating activities do not generate enough cash to stay liquid. This can happen if profits are tied up in outstanding accounts receivable and overstocked inventory or if a company spends too much on capital expenditures.
A global manufacturing company found that mismatched and inconsistent customer and supplier payment terms across divisions and regions were causing problems with its cash flow. It used master data management to standardize payment terms and enforce those terms on contracts, invoices, and purchase orders, which better balanced the timing of cash coming in and going out. The company also found that delays in collecting payments were impacting cash flow. Two of the biggest problems causing delays were incorrect billing and tax information. Master data management helps the manufacturer ensure the billing and tax information was captured and validated as part of the customer record.
Days sales outstanding (DSO) is the average number of days it takes a company to convert credit sales into cash by collecting on account receivables. It’s a metric that chief financial officers watch closely because of its impact on earnings and cash flow. Let’s look at how master data management can help address some of the common causes of issues with DSO.
Master data management helps you ensure you have accurate and complete billing and contact data, which reduces delays in invoices being delivered to the correct location and person. It can help you ensure you have accurate and complete price, purchase order and tax data, which reduces invoice disputes. On-time and in-full order deliveries are another issue that impacts DSO. Master data management helps you ensure you have timely and accurate inventory, manufacturing, and shipping data, which helps improve the accuracy of delivery date quotes.
Days inventory outstanding (DIO) measures the average length of time that a company’s cash is locked up in the inventory. Since inventory represents cash unavailable to grow the business or pay expenditures, a smaller DIO number is generally preferred. Managing DIO is a balance between having enough inventory to meet forecasted demand without having so much inventory that you miss opportunities for using the cash (or have excessive markdowns and write-offs). Rising DIO can be an indicator of softness in demand from changing customer preferences and issues in marketing and sales. It is also possible that a company may retain high inventory levels to achieve high order fulfillment rates, such as in anticipation of supply shortages or strong holiday season demand.
Accurate master data can help you get visibility into inventory across plants, divisions, and regions to better manage inventory turnover. By analyzing the DIO, you can see which products are performing well and which aren’t. Management can then take action to improve sales for products with increasing DIO or drop poor performers entirely.

Get Started: Improve Digital Commerce with Master Data Management
In this blog post, I defined digital commerce and three measures for success: revenue generation, cost management, and cash flow. Then I gave you examples of how master data management can help improve those three measures. (And remember, this post was by no means an exhaustive list.)
Master data management can help you increase basket size through better product recommendations, decrease returns, and improve overall equipment effectiveness. One of the keys to success is to identify opportunities for improvement – start small and get some early success, so you can expand your improvements across the entire digital commerce value chain.
To learn more about how Informatica can help you with digital commerce, watch the Data Management for Supplier & Product webinar – available now on demand.








