How to Choose Between Application Layer and Database Layer for SAP Data Integration
Last Published: Nov 19, 2024 |
Table Of Contents
Data is at the heart of business transformation, and data analytics are essential to achieve successful business outcomes. On top of that, analytics tools have become highly transformative technologies in recent years.
As an SAP customer, you exemplify this trend. To maximize your investments and enhance decision-making, you need a holistic view of all your enterprise data. This includes analyzing SAP data alongside information from other hybrid and multi-cloud enterprise applications and data sources. However, extracting data from SAP systems, integrating it into a modern, scalable data analytics platform and combining it with various first-party and third-party data sources to generate new insights can be complex and challenging.
While extracting data from SAP systems, you may face the choice between two main options: the application layer and the database layer. Each has advantages and disadvantages, making the decision dependent on specific business needs and technical requirements. Let's explore the pros and cons of each option to help you make an informed decision.
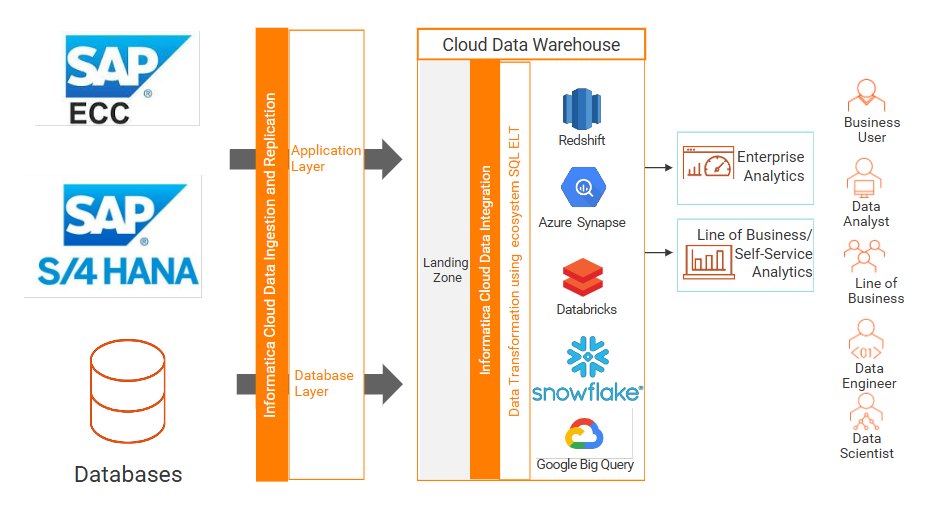
Figure: SAP Data Integration through application and database layer.
Option 1: Application Layer
The application layer option involves extracting data directly from the application level, utilizing SAP's business and application logic.
Pros:
- Low-level to high-level data models: This option supports a wide range of data models, from detailed transactional data to aggregated business intelligence data.
- Business and application logic: The data extracted includes built-in SAP business logic, making it more meaningful and easier to use in downstream applications.
- SAP runtime license sufficient: Typically, only the SAP runtime license is needed, potentially reducing licensing costs compared to other methods.
- Lower cost of data management: For high-level data, fewer tables and pipelines are needed, reducing the cost of data ingestion, postprocessing, and storage.
Cons:
- May not be suitable for real-time ingestion: This method is generally not suitable for scenarios requiring near real-time data updates due to its slower processing nature.
- Performance considerations: May experience slower performance with very large datasets compared to direct database access.
- Development overhead: Initial setup and configuration can be more involved than direct access.
- Higher load on SAP system: Extracting data at the application layer may increase the load on the primary SAP system, potentially affecting overall system performance.
Option 2: Database Layer
The database layer option involves directly accessing the underlying database tables of the SAP system.
Pros:
- Minimal impact on source system: Extracting data from the database layer (via a log-based approach) has a relatively lower impact on the source SAP system's performance.
- Fast and high performance: This method is the fastest and most efficient way to retrieve data from SAP, providing high performance for large-scale data extraction tasks.
Cons:
- Lack of business or application logic: The data extracted does not include SAP's business and application logic, which may require additional processing to make it useful.
- Low-level data model: The data is often in a low-level format, which can be more complex and harder to interpret without additional context. However, it also allows detailed custom analysis.
- SAP enterprise license requirement: Accessing data at the database level may require an SAP enterprise license, potentially increasing costs.
Informatica Connectors for SAP Data Integration
Informatica offers multiple, easy-to-use connectors to extract data without the need to write code or possess the deep knowledge necessary to work with SAP systems. You can extract the data in batch, micro batch or near real-time, depending on your use cases. Informatica has a strong presence in cloud and on-premises data management, making it one of the best tools for your data projects.
ABAP Table Reader is one of the most versatile connectors, giving a relational interface to all SAP tables and views. You can join and filter them just like any other relational database while connecting to the application layer; our customers move trillions of records using this interface daily. ABAP Delta Reader is an add-on module on top of the ABAP Table Reader that captures the deltas or changes based on the SAP Change Documents. Given that many SAP base tables do not track the timestamps, this functionality comes in handy to pull changes into data warehouses and data lakes.
SAP IDoc listener can extract data in near real-time for the most time sensitive data elements. Informatica can be used both as an ETL and ELT tool based on the use case at hand.
Informatica also has many other connectors like BAPI/RFC, ODP, OData v2, OData v4, BEx Query and BW Connector, Datasphere, SuccessFactors, Ariba to meet all your extended needs.
For incremental data and CDC use cases, the Cloud Data Ingestion and Replication (CDIR) service can be used. CDIR is a no-code, wizard-driven, intuitive, unified cloud-native service that can seamlessly ingest and replicate data from SAP ECC or SAP S/4HANA to virtually any on-premises or cloud target. This service comes with out-of-the-box connectivity that includes SAP Mass Ingestion and Hana DB connectors, which leverage log-based and trigger approaches.
For use cases demanding real-time data and minimal system impact, the Database Layer is preferable. However, if you need data enriched with business logic along with periodic updates, the Application Layer might be the better choice. Evaluate your requirements carefully to choose the most suitable option for your SAP data extraction needs.
Next Steps
Both the application layer and database layer options have their strengths and weaknesses. The choice depends on your specific use case, including the required data update frequency, system performance impact and the need for business logic in the extracted data.
The Informatica Intelligent Data Management Cloud (IDMC) simplifies the process of accessing and integrating data from multiple interfaces within an SAP environment to give users access to the right information at the right time in the right interface for decision-making. By accelerating the availability of information and driving operational efficiency, you will be able to make decisions faster with more confidence.
Learn more about Cloud Data Ingestion and Replication and Cloud Data Integration. Better yet, get started with a free 30-day trial.